Artificial Intelligence (AI) and emerging technologies are already reshaping the global economy. From healthcare to finance, robotics to cloud computing, these sectors are transforming business models and opening up unique opportunities for investors. In this complete guide, you will learn why and how to invest in AI, discover the best strategies, and access company and ETF analyses.

🧠 Understanding AI and Emerging Technologies
Before investing in Artificial Intelligence (AI), it is essential to clearly understand what it is, how it works, and how it connects with other emerging technologies. This knowledge will not only help you identify strong opportunities but also avoid common investment pitfalls.
What Is Artificial Intelligence?
Artificial Intelligence refers to the ability of machines to simulate human intelligence and decision-making. Rather than being a single technology, AI encompasses a wide range of methods and systems designed to analyze data, learn from it, and adapt over time.
Key subfields of AI
Artificial intelligence encompasses several core subfields, each contributing to different aspects of innovation:
| Subfields | Description |
|---|---|
| Machine Learning | Focuses on developing algorithms that can recognize patterns in data and improve their performance over time without explicit programming. |
| Deep Learning | A specialized area within ML that uses multi-layered neural networks to process massive datasets and is particularly effective in applications such as image recognition, speech processing, and generative AI. |
| Natural Language Processing | Enables machines to understand, interpret, and generate human language, making interactions with systems like ChatGPT possible. |
| Computer Vision | Equips machines with the ability to analyze, interpret, and respond to visual information from the world around them. Finally. |
| Robotics and Automation | A specialized area within ML that uses multi-layered neural networks to process massive datasets and is particularly effective in applications such as image recognition, speech processing, and generative AI. |
The Broader World of Emerging Technologies
AI does not exist in isolation. It is part of a larger digital transformation that involves multiple interconnected technologies. Successful AI investment often depends on these supporting pillars:
| Activities | Description | Leaders |
|---|---|---|
| Cloud Computing | Provides the infrastructure for training and deploying AI models at scale. | Oracle, Amazon, CoreWeave, DXC, Snowflake, ServiceNow, Teradata |
| Semiconductors & GPUs | Specialized chips power AI algorithms by handling massive computations efficiently | Nvidia, Marvell, Broadcom, AMD, QUALCOMM, NXP, Intel |
| Cybersecurity | As AI grows, so does the need to protect data and networks from increasingly sophisticated threats. | Okta Identity Cloud, DXC Technology, CyberArk Software, Zscaler Internet Access, Fortinet |
| Robotics & Automation | The convergence of AI with physical machinery is revolutionizing industries such as manufacturing, logistics, and healthcare. | Cadence Design Systems, Pegasystems, ServiceNow, Synopsys, UiPath |
| Quantum Computing | Still in its early stages, it has the potential to accelerate AI capabilities significantly. | IBM, Quantum Computing |
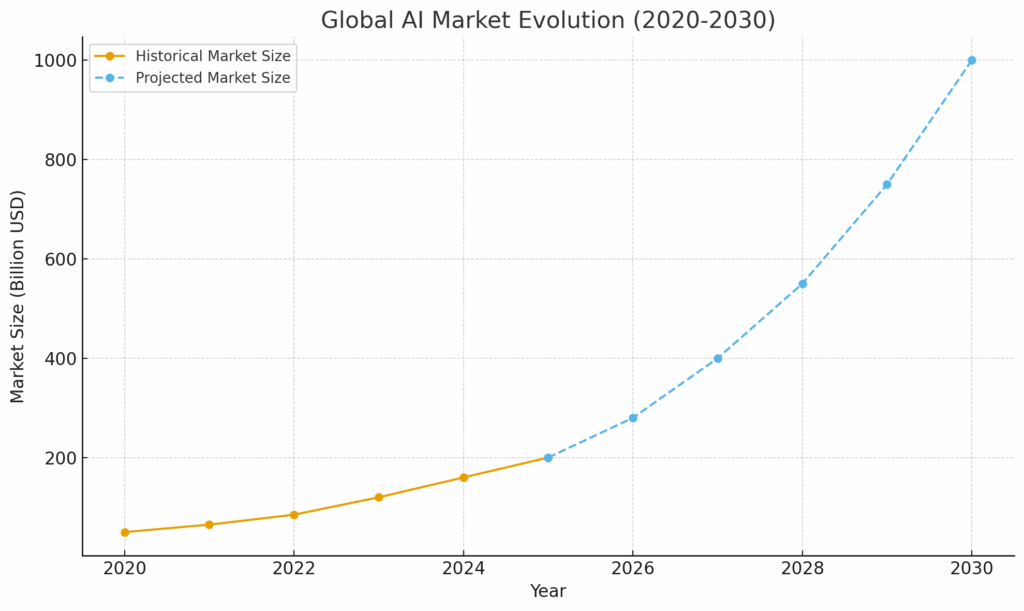
Market Growth and Projections
The AI market is experiencing explosive growth. In 2025, the global AI market is valued at over $200 billion, and projections suggest it could exceed $1 trillion by 2030. This growth is fueled by:
- The adoption of AI in everyday products and services (intelligent assistants, recommendation systems, and autonomous vehicles).
- Business use cases in finance, healthcare, retail, and manufacturing.
- Massive investments from both governments and private companies in AI R&D.
For investors, this means AI is no longer a niche—it is becoming a critical driver of global economic growth. However, high growth also attracts speculation, making it essential to distinguish between solid long-term plays and overhyped trends.
Industries Being Transformed by AI
AI is not just a technological innovation—it is fundamentally reshaping entire industries, driving efficiency, enhancing decision-making, and creating new opportunities across multiple sectors.
| Industry | Description | Actors |
|---|---|---|
| Healthcare | Diagnostics, drug discovery, and personalized medicine. | GE HealthCare, Intuitive Surgical, Tempus AI |
| Finance | Algorithmic trading, fraud detection, and robo-advisors | Upstart Holdings, StoneCo, Workday |
| Transportation | Autonomous vehicles, smart logistics, and drones | Tesla, Pony AI, Uber Technologies, Ambarella |
| Retail & Marketing | Recommendation engines, customer insights, demand forecasting | AppLovin, Salesforce, Shopify, Wix |
| Manufacturing | Predictive maintenance, robotics, and supply chain optimization | Cadence Design Systems, Pegasystems, ServiceNow, Synopsys, UiPath |
✅ Key Takeaway
Understanding AI means more than knowing the buzzwords. It requires recognizing how AI integrates with other technologies and how it reshapes industries worldwide. For investors, this context is crucial: it helps you identify sustainable opportunities while being mindful of the risks associated with overvaluation.
💡 Why Invest in AI and Tech?
Artificial Intelligence and technology are not just trends—they are structural shifts shaping the global economy. From powering daily consumer products to driving large-scale industrial transformation, AI is becoming a core driver of productivity and innovation. For investors, this creates both high-growth opportunities and unique risks that must be evaluated carefully.
Strong Growth Potential
The AI and tech sectors have consistently outperformed the broader market over the past decade. Companies that embraced AI early—such as Nvidia, Microsoft, Alphabet, and Amazon—have delivered outsized returns compared to traditional industries.
Key reasons for future growth include:
- Rapid adoption of AI across industries (healthcare, finance, retail, logistics).
- Increasing reliance on data-driven decision-making.
- Continuous breakthroughs in hardware (GPUs, chips) and software (large language models, generative AI).
- Expanding government and private investment in AI research and development.
Global Economic Impact
By 2030, AI is expected to contribute up to $15.7 trillion to the global economy (PwC report). This makes it one of the most transformative forces of our time, on par with the industrial revolution and the rise of the internet.
Examples of AI-driven impact:
- Productivity gains: AI automates repetitive tasks, reducing costs.
- Innovation cycles: faster drug discovery, smarter supply chains, advanced robotics.
- Job transformation: while some roles may disappear, entirely new careers in AI engineering, data science, and ethics are emerging.
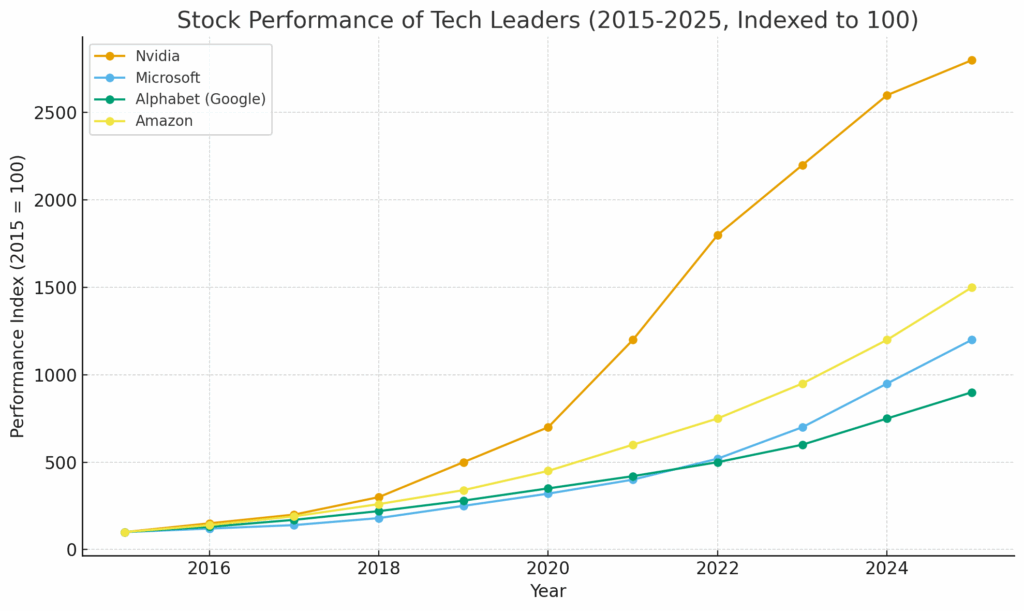
Historical Performance of Tech Leaders
Investors who backed tech pioneers early have seen exponential returns. For example, Nvidia’s market capitalization grew from $10 billion in 2010 to over $2 trillion by 2025, fueled by its leadership in GPUs for AI. Similarly, Microsoft reinvented itself around cloud and AI, delivering strong and steady growth.
Risks and Challenges
While the upside is huge, AI and tech are not risk-free. Many companies are overvalued, and hype cycles often lead to bubbles. Investors must balance optimism with caution.
Main risks include:
- Regulation: governments may impose restrictions on AI applications, particularly in areas such as data privacy and defense.
- Overvaluation: some AI stocks trade at very high price-to-earnings ratios, increasing volatility.
- Competition: the sector is crowded, with startups and tech giants fighting for dominance.
- Technological uncertainty: not all innovations succeed, and some may be replaced quickly.
✅ Key Takeaway
Investing in AI and technology can generate significant long-term returns, but it requires a strategic approach. The strongest opportunities lie in companies with sustainable business models, competitive advantages, and robust research and development (R&D) investments. At the same time, diversification and risk management are essential to avoid exposure to speculative bubbles.
📈 Different Ways to Invest
There is no single way to invest in Artificial Intelligence and emerging technologies. Depending on your risk tolerance, time horizon, and capital, you can choose between direct investments in companies, diversified funds, or alternative vehicles. Below are the main approaches to consider.
1. Individual Stocks
Buying shares of companies directly involved in AI gives you exposure to high-growth leaders, but it also requires careful stock-picking and analysis.
Examples of AI-driven stocks:
| Big Tech leaders | Specialized players | Hardware enablers |
|---|---|---|
| Nvidia (semiconductors & GPUs) Microsoft (cloud & AI integration) Alphabet (AI research & search engines) Amazon (cloud AI, logistics optimization). | Palantir (data analytics) DocuSign (electronic signature) UiPath (robotic process automation) C3.ai (enterprise AI solutions). | ASML (semiconductor lithography) AMD (chip design) Super Micro Computer (server solutions) Seagate Technology (data storage) |
⚠️ Investor note: Individual stocks are often volatile. A company’s success depends on execution, market share, and long-term innovation, so due diligence is essential.
2. Exchange-Traded Funds (ETFs)
For those who prefer diversification and lower risk, ETFs are one of the best ways to invest in the AI sector. They pool multiple companies into a single investment vehicle, reducing exposure to the failure of any one stock.
Popular AI and Tech ETFs include:
| Ticker | Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| AIQ | Global X Artificial Intelligence & Technology ETF | Diversified across global AI leaders. |
| IRBO | iShares A.I. Innovation and Tech Active ETF | Exposure to companies innovating in AI and robotics. |
| ROBO | ROBO Global Robotics & Automation ETF | Focuses on robotics and automation. |
| ROBT | First Trust Nasdaq Artificial Intelligence and Robotics ETF | Tracks companies in AI, robotics, and automation. |
| WTAI | WisdomTree Artificial Intelligence and Innovation ETF | AI and innovation companies. |
| AIEQ | Amplify AI Powered Equity ETF | Focuses on AI companies. |
| IVES | Dan Ives Wedbush AI Revolution ETF | Selection of the 30 leading AI companies. |
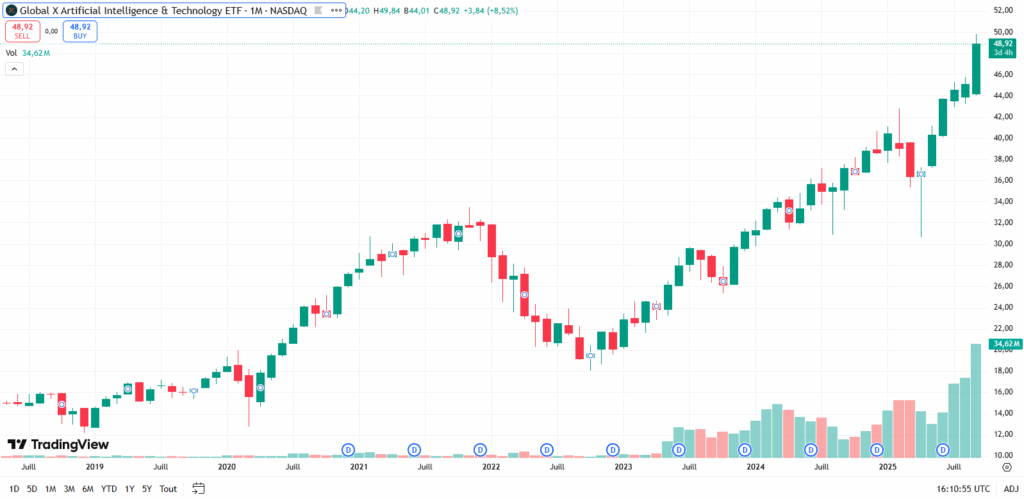
Global X Artificial Intelligence & Technology price chart
⚠️ Investor note: ETFs offer safety in diversification but may dilute returns compared to investing directly in top-performing stocks.
3. Mutual Funds and Private Equity
Investors looking to gain exposure to artificial intelligence have multiple options. Beyond individual stocks, a growing number of mutual funds and private equity firms focus specifically on AI and related technologies. These funds provide diversified access to companies building AI infrastructure, developing innovative applications, and driving adoption across industries.
Mutual Funds with AI Exposure
| Fund | AI Focus / Strategy | Region |
|---|---|---|
| BlackRock BGF AI Innovation Fund | A thematic global equity fund centered on artificial intelligence and digital innovation. | Europe |
| Fidelity Select Technology Portfolio (FSPTX) | Holds tech and AI leaders such as Microsoft, Nvidia, and Alphabet. | U.S. |
| DWS Science and Technology Fund (KTCAX) | Invests in companies driving AI and semiconductor innovation. | Global |
| Janus Henderson Global Technology and Innovation Fund (JNGTX) | Focus on disruptive technologies, with a large AI allocation. | Global |
| Axis Growth Opportunities Fund | Mix of large- and mid-cap companies with AI exposure (e.g., Microsoft, Alphabet, Tata Elxsi). | India |
| SBI Focused Equity Fund | Concentrated portfolio including AI-driven global tech players. | India |
| Parag Parikh Flexi Cap Fund | Allocates ~15–20% to AI-related U.S. tech giants. | India |
| Kotak Small Cap Fund | Includes small-cap firms in analytics, robotics, and AI applications. | India |
Private Equity & Venture Capital Focused on AI
| Private Equity | AI Focus / Strategy | Region |
|---|---|---|
| MGX I | A large new private equity fund dedicated to AI infrastructure, chips, and data centers. | Abu Dhabi |
| Greycroft | Venture capital firm with AI investments such as Stability AI and Contextual AI. | U.S. |
| Kedaara Capital | invested $240M in Axtria, an AI-driven life sciences data analytics company. | India |
| Sequoia Capital | Active across AI startups, including Anthropic, Hugging Face, and Gong. | U.S. |
| Andreessen Horowitz (a16z) | Significant investments in generative AI companies (e.g., OpenAI, Character.ai). | U.S. |
| SoftBank Vision Fund | Venture capital firm with investments in AI companies such as Stability AI and Contextual AI. | England |
⚠️ These options usually require higher minimum capital and are less liquid compared to ETFs or stocks.
4. Blockchain and AI-Linked Cryptocurrencies
An emerging area is the intersection of AI and blockchain. Some projects aim to decentralize AI infrastructure or create marketplaces for AI models. Although this space is highly speculative, it is attracting attention from investors seeking alternative investment opportunities.
Examples include:
- Hut 8 Corp: a prominent player in the cryptocurrency mining sector.
- SingularityNET (AGIX): decentralized AI services marketplace.
- Fetch.ai (FET): AI-powered digital agents on blockchain.
⚠️ Investor note: crypto markets are extremely volatile and unregulated in many regions—allocate only what you can afford to lose.
✅ Key Takeaway
From individual stocks to diversified ETFs, private equity, and even blockchain projects, investors have multiple ways to gain exposure to AI. The best approach depends on your strategy:
- For long-term steady growth → ETFs or blue-chip tech stocks.
- For higher risk/reward → specialized stocks, startups, or crypto.
- For diversification → a mix of these vehicles.
🆚 Pure-play AI vs AI-powered companies
When evaluating investment opportunities, it is essential to distinguish between pure-play AI companies and AI-powered companies. Understanding this distinction will help you differentiate between businesses whose growth is entirely tied to AI and those that leverage it as part of a broader strategy.
Difference between pure-play AI companies and AI-powered companies
- Pure-play AI companies build their entire business model around artificial intelligence, offering products and services where AI is the primary value driver—examples include firms specializing in enterprise AI platforms, generative AI models, or AI-optimized hardware. A pure-play company monetizes its proprietary AI algorithms directly.
- AI-powered companies operate in broader industries such as software, e-commerce, or finance, where AI is integrated as a tool to enhance their core offerings. An AI-powered company utilizes AI to improve customer experience, streamline operations, or boost productivity.
Pure-play AI &AI-powered comparison
The table below highlights the key differences between pure-play AI companies and AI-powered businesses:
| Pure-Play AI Companies | AI-Powered Companies | |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Businesses whose core product or service is artificial intelligence itself. | Businesses in other sectors that use AI to enhance or scale their core offerings. |
| Business Model | Generate revenue directly from AI platforms, models, or infrastructure. | Monetize products or services in industries like SaaS, e-commerce, or fintech, with AI as a supporting tool. |
| Investor Takeaway | High exposure to AI growth, but often higher risk and volatility since their success is fully tied to AI adoption. | Broader business models with more stability, but less “pure” exposure to AI’s explosive growth. |
Pure-play AI companies
| Ticker | Name | Company Description |
|---|---|---|
| AI | C3.ai | Provides a comprehensive suite of AI applications and platforms. |
| BBAI | BigBear.ai | Provides artificial intelligence and machine learning solutions designed to enhance decision-making processes. |
| CRWV | CoreWeave | Operates a cloud platform that provides scaling, support, and acceleration for generative AI applications. |
| DARK.LON | Darktrace | Protecting organizations from sophisticated digital threats with an AI-based cybersecurity platform. |
| ALTAI.PA | LightOn SA | Specializing in the development of generative artificial intelligence software solutions. |
| PERF | Perfect Corp. | Provides software solutions that leverage artificial intelligence and augmented reality to enhance the beauty and fashion industries. |
| PONY | Pony.ai | Provides robotruck and robotaxi services, which include a range of autonomous vehicle (AV) engineering solutions. |
| SOUN | SoundHound | Developing voice artificial intelligence (AI) platforms. |
AI-powered companies
| Ticker | Name | Company Description |
|---|---|---|
| ADBE | Adobe | Adobe Inc. operates as a diversified software company worldwide, primarily through three segments: Digital Media, Digital Experience, and Publishing and Advertising. |
| GOOG | Alphabet | Alphabet Inc. operates in the technology sector, primarily focusing on internet content and information. |
| AMZN | Amazon.com | Amazon.com, Inc. engages in the retail sale of consumer products and subscriptions through online and physical stores in North America and internationally. |
| DOCU | DocuSign | DocuSign, Inc. operates in the Software – Application industry, providing electronic signature solutions that facilitate the digital management of agreements. |
| MSFT | Microsoft | Microsoft Corporation develops, licenses, and supports software, services, devices, and solutions worldwide. |
| NVDA | NVIDIA | NVIDIA Corporation is a global leader in graphics processing technology, providing innovative solutions for gaming, professional visualization, data centers, and automotive markets. |
| PLTR | Palantir Technologies | Palantir Technologies Inc. builds and deploys software platforms for the intelligence community to assist in counterterrorism investigations and operations in the United States, the United Kingdom, and internationally. |
| CRM | Salesforce | Salesforce, Inc. is a technology company that specializes in customer relationship management (CRM) software. |
| SNPS | Synopsys | Synopsys, Inc. specializes in electronic design automation software products that facilitate the design and testing of integrated circuits. |
| TSLA | Tesla | Tesla, Inc. designs, develops, manufactures, leases, and sells electric vehicles and energy generation and storage systems globally. |
| PATH | UiPath | UiPath Inc. provides an end-to-end automation platform that offers a range of robotic process automation (RPA) solutions primarily in the United States, Romania, and Japan. |
| VERI | Veritone | Veritone, Inc. is a technology company that specializes in artificial intelligence computing solutions. |
🔍 How to Analyze an AI Company
Evaluating an AI company requires a different lens than analyzing traditional businesses. While financial metrics remain essential, the true value of an AI-driven enterprise often lies in its intellectual property, talent pool, and technological edge. Here are the key dimensions to consider:
1. Business Model & Revenue Streams
The first step is to understand how the company generates income. Is it selling AI software as a service (SaaS), licensing algorithms, providing consulting services, or monetizing data? Some firms focus on vertical integration (e.g., healthcare AI solutions), while others target broad applications across multiple industries. A diversified, recurring revenue model—particularly subscription-based—often signals long-term resilience.
2. Technology & Innovation Edge
AI companies thrive or fail based on their ability to innovate. Assess whether the company is developing proprietary algorithms, building scalable platforms, or merely repackaging open-source tools. Patents, research partnerships, and published breakthroughs can be strong indicators of technological leadership. Cutting-edge capabilities in areas such as deep learning, natural language processing (NLP), or computer vision often create defensible competitive advantages.
3. Data Assets & Accessibility
AI systems thrive on data. A company with exclusive access to large, high-quality datasets often holds a strategic advantage. For example, firms in autonomous driving (like Waymo or Tesla) continuously refine algorithms through millions of real-world driving miles. Understanding whether the company owns its data, licenses it, or relies on third parties is crucial to evaluating sustainability.
4. Talent & Leadership Team
AI is a talent-driven field. Evaluate the expertise of the founding team, engineers, and data scientists. Leaders with strong academic or industry track records in AI, machine learning, or computer science often inspire investor confidence. Employee retention and the ability to attract top talent also provide insight into the company’s culture and long-term innovation potential.
5. Market Opportunity & Scalability
Not all AI companies operate in equally lucrative markets. Analyzing the total addressable market (TAM) helps determine growth potential. Is the company targeting niche industries with limited upside, or is it solving broad, cross-sector problems? Scalability is critical: AI solutions should be adaptable across regions, industries, or customer segments to maximize expansion opportunities.
6. Partnerships & Ecosystem
AI companies rarely operate in isolation. Strategic alliances with cloud providers, hardware manufacturers, or enterprise clients often amplify growth. Partnerships with industry leaders (e.g., Nvidia, Microsoft, AWS) can accelerate credibility, distribution, and adoption.
7. Financial Health & Growth Metrics
While early-stage AI startups may not be profitable, key indicators to watch include revenue growth, R&D investment, customer acquisition costs, and gross margins. A healthy balance between aggressive innovation and financial discipline is vital for long-term sustainability.
8. Regulation, Ethics & Risk Management
AI is increasingly under regulatory scrutiny, particularly regarding data privacy, bias, and transparency. Companies that proactively implement ethical AI frameworks and comply with evolving laws (such as the EU AI Act or U.S. regulations) will likely face fewer long-term risks. Investors should consider how a company addresses these challenges to avoid reputational or legal pitfalls.
✅ Key Takeaway
Analyzing an AI company goes beyond quarterly earnings reports. It requires understanding the interplay between innovation, data, people, and market strategy. The most promising firms are those that combine cutting-edge technology with scalable business models and responsible governance.
🏁 Conclusion
Investing in Artificial Intelligence and emerging technologies offers unparalleled opportunities, but it also demands careful analysis and strategic thinking. From understanding the fundamentals of AI and its supporting technologies to evaluating market potential, financial health, and innovation capabilities, investors must approach this rapidly evolving sector with both optimism and caution.
The strongest opportunities lie in companies that combine cutting-edge technology, scalable business models, robust R&D, and ethical governance. Diversifying across individual stocks, ETFs, private equity, and even blockchain projects can help balance risk while maximizing growth potential.
Ultimately, AI is more than a trend—it is a transformative force shaping the global economy. By equipping yourself with knowledge, leveraging sound investment strategies, and staying attuned to market and technological developments, you can position your portfolio to capture the long-term benefits of this next wave of innovation.
✅ Key takeaway: Strategic, informed investment in AI and emerging technologies can yield significant long-term rewards, provided you combine research, risk management, and diversification.
For more insights, you can explore our detailed company analyses directly on Artificall.com.