Home > Analyses > Technology > International Business Machines Corporation
International Business Machines Corporation (IBM) powers critical operations across industries, embedding itself in daily business infrastructure worldwide. With leadership in hybrid cloud, AI, and enterprise software, IBM continually redefines technology services through innovation and strategic acquisitions like Red Hat. Its broad consulting and infrastructure footprint underpins global digital transformation. As markets evolve rapidly, I question whether IBM’s current fundamentals can sustain its premium valuation and deliver long-term growth amid intensifying competition.

Table of contents
Business Model & Company Overview
International Business Machines Corporation, founded in 1911 and headquartered in Armonk, NY, commands a dominant position in information technology services. It delivers an integrated ecosystem spanning software, consulting, infrastructure, and financing, creating seamless solutions for complex enterprise needs. This legacy firm drives innovation through hybrid cloud, AI, and security software, underpinning mission-critical operations worldwide.
IBM’s revenue engine balances recurring software licenses and consulting fees with hardware sales and financing services. Its strategic footprint spans the Americas, Europe, and Asia, enabling tailored solutions in regulated industries like banking and retail. The company’s economic moat lies in its comprehensive, end-to-end technology platform that shapes the future of enterprise IT.
Financial Performance & Fundamental Metrics
I will analyze International Business Machines Corporation’s income statement, key financial ratios, and dividend payout policy to assess its fundamental strength and sustainability.
Income Statement
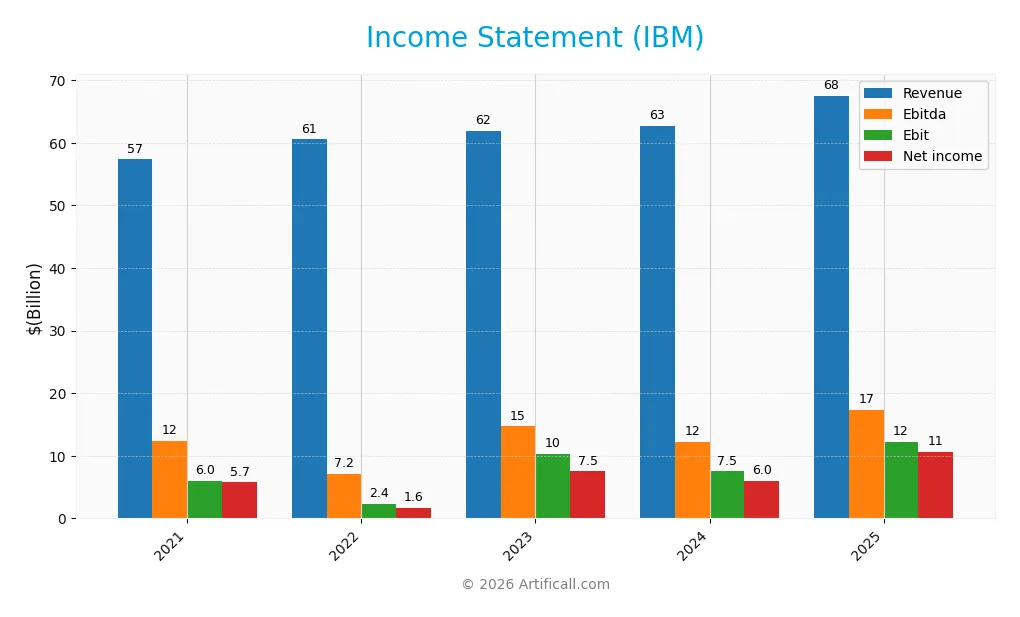
Below is IBM’s income statement for the fiscal years 2021 through 2025, showing key profitability and expense figures in USD.
| 2021 | 2022 | 2023 | 2024 | 2025 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Revenue | 57.4B | 60.5B | 61.9B | 62.8B | 67.5B |
| Cost of Revenue | 25.9B | 27.8B | 27.6B | 27.2B | 27.4B |
| Operating Expenses | 24.6B | 24.5B | 24.5B | 25.5B | 29.9B |
| Gross Profit | 31.5B | 32.7B | 34.3B | 35.6B | 40.2B |
| EBITDA | 12.4B | 7.2B | 14.7B | 12.2B | 17.3B |
| EBIT | 6.0B | 2.4B | 10.3B | 7.5B | 12.3B |
| Interest Expense | 1.2B | 1.2B | 1.6B | 1.7B | 1.9B |
| Net Income | 5.7B | 1.6B | 7.5B | 6.0B | 10.6B |
| EPS | 6.41 | 1.82 | 8.23 | 6.53 | 11.36 |
| Filing Date | 2022-02-22 | 2023-02-28 | 2024-02-26 | 2025-02-25 | 2026-01-28 |
Income Statement Evolution
From 2021 to 2025, IBM’s revenue rose by 17.8%, signaling steady top-line growth. Net income surged 84.5%, reflecting strong profitability gains. Gross margin remained robust at 59.5%, while EBIT margins expanded significantly, indicating improved operational efficiency. The net margin also improved markedly, underscoring sustained margin enhancement amid rising revenues.
Is the Income Statement Favorable?
In 2025, IBM reported $67.5B in revenue with a 7.6% year-over-year increase, considered neutral growth. Net income jumped 76%, driving a net margin of 15.7%, which is favorable. EBIT growth of 63% highlights operational leverage despite a slight unfavorable trend in operating expenses relative to revenue. Overall, the income statement fundamentals appear solid and largely favorable.
Financial Ratios
The table below summarizes key financial ratios for International Business Machines Corporation (IBM) over the last five fiscal years:
| Ratios | 2021 | 2022 | 2023 | 2024 | 2025 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Net Margin | 10.0% | 2.7% | 12.1% | 9.6% | 15.7% |
| ROE | 30.4% | 7.5% | 33.3% | 22.1% | 32.4% |
| ROIC | 6.3% | 8.1% | 7.8% | 9.2% | 8.6% |
| P/E | 20.9 | 77.5 | 19.9 | 34.2 | 26.1 |
| P/B | 6.3 | 5.8 | 6.6 | 7.5 | 8.5 |
| Current Ratio | 0.88 | 0.92 | 0.96 | 1.04 | 0.93 |
| Quick Ratio | 0.83 | 0.87 | 0.93 | 1.00 | 0.90 |
| D/E | 2.9 | 2.5 | 2.7 | 2.1 | 2.1 |
| Debt-to-Assets | 41.8% | 42.4% | 44.3% | 42.6% | 44.2% |
| Interest Coverage | 5.9 | 6.7 | 6.1 | 5.9 | 5.3 |
| Asset Turnover | 0.43 | 0.48 | 0.46 | 0.46 | 0.44 |
| Fixed Asset Turnover | 6.4 | 7.4 | 7.1 | 7.0 | 7.5 |
| Dividend Yield | 4.9% | 4.7% | 4.1% | 3.0% | 2.3% |
Evolution of Financial Ratios
From 2021 to 2025, IBM’s Return on Equity (ROE) showed significant improvement, rising from 30.38% to 32.45%, reflecting enhanced profitability. The Current Ratio fluctuated below the ideal threshold, averaging near 0.93 in 2025, indicating weaker short-term liquidity. Debt-to-Equity ratio improved moderately but remained high at 2.06 in 2025, signaling sustained leverage levels.
Are the Financial Ratios Fovorable?
In 2025, IBM’s profitability ratios like net margin (15.69%) and ROE (32.45%) are favorable, supported by a solid interest coverage ratio of 6.34. Liquidity ratios present mixed signals: the current ratio at 0.93 is unfavorable, while the quick ratio is neutral. Leverage remains a concern with a debt-to-equity ratio of 2.06 deemed unfavorable. Market valuation ratios such as P/E and P/B are also unfavorable, resulting in an overall slightly favorable financial profile.
Shareholder Return Policy
International Business Machines Corporation (IBM) maintains a dividend payout ratio near 60%, with a stable dividend per share around $6.7 and an annual yield of about 2.3%. The payout is well-covered by free cash flow, supported by consistent operating cash flow and manageable capital expenditures.
IBM also conducts share buybacks, complementing dividends to return capital to shareholders. This balanced approach, supported by solid cash generation, aligns with sustainable long-term value creation, though investors should monitor leverage levels that could pressure future distributions.
Score analysis
The radar chart below displays key financial scores for International Business Machines Corporation (IBM):
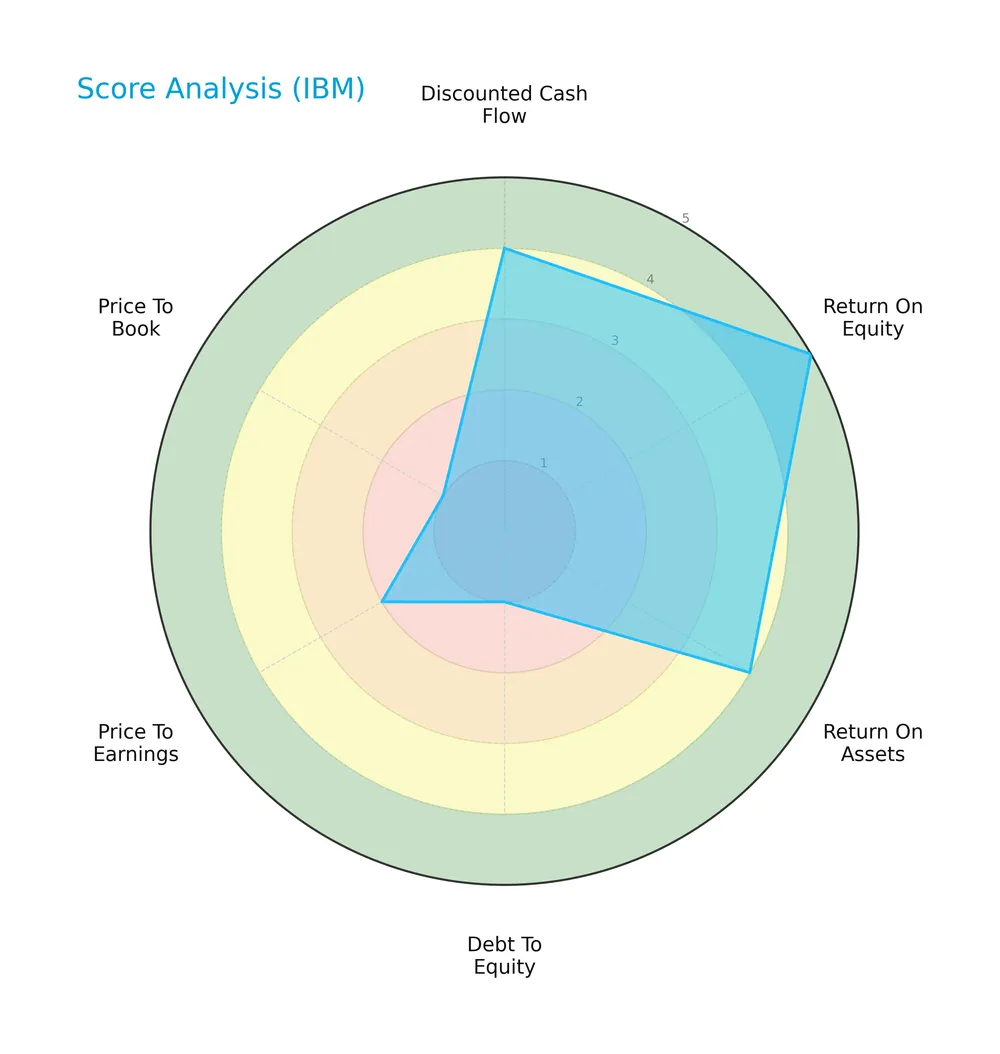
IBM shows strong profitability with a very favorable ROE score of 5 and favorable ROA of 4. Its discounted cash flow score is favorable at 4. However, leverage and valuation metrics are weak, with very unfavorable debt-to-equity and price-to-book scores of 1, and a moderate price-to-earnings score of 2.
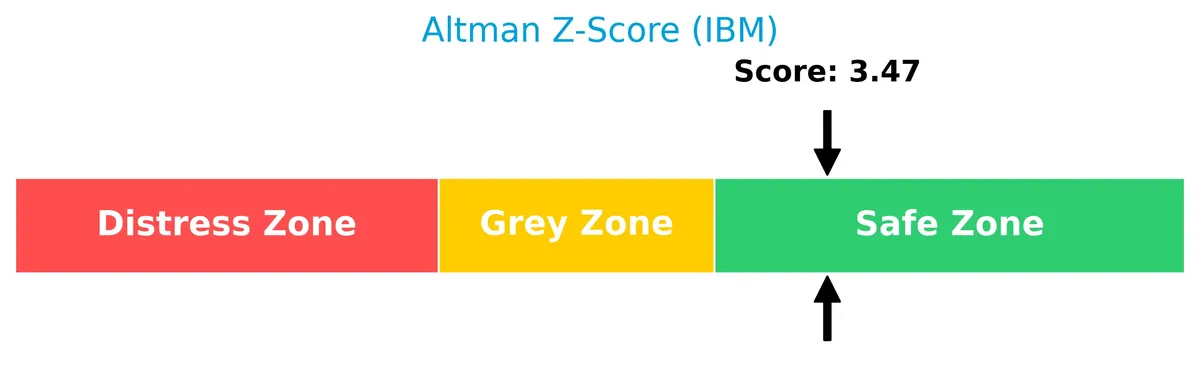
Analysis of the company’s bankruptcy risk
IBM’s Altman Z-Score places it in the safe zone, indicating a low risk of bankruptcy based on financial stability factors:
Is the company in good financial health?
The Piotroski Score chart illustrates IBM’s overall financial strength:
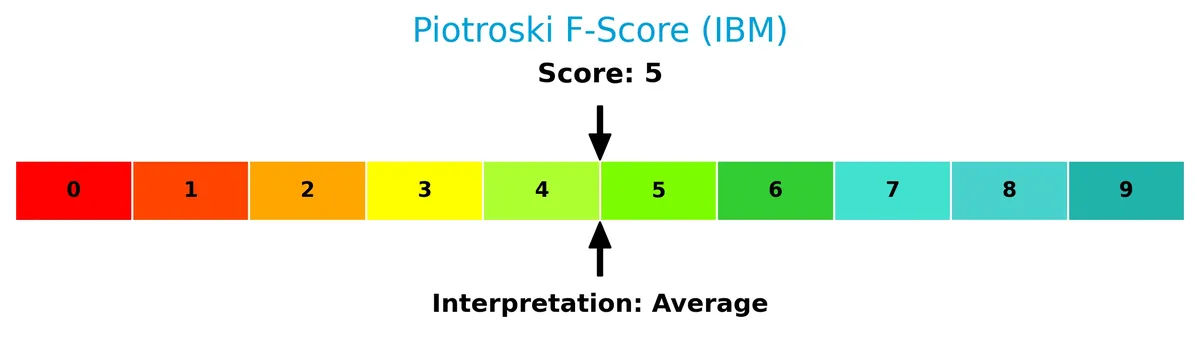
With a Piotroski Score of 5, IBM falls into the average category. This suggests moderate financial health, with room for improvement in profitability, leverage, and efficiency metrics to strengthen its investment appeal.
Competitive Landscape & Sector Positioning
This analysis examines International Business Machines Corporation’s strategic positioning within the technology sector. We will review its revenue breakdown, key products, and main competitors. I will assess whether IBM holds a competitive advantage over its industry peers.
Strategic Positioning
IBM maintains a diversified portfolio across Software (27B), Consulting (21B), Infrastructure (14B), and Financing (0.7B) segments. Geographically, revenue is well-distributed with Americas (31B), EMEA (19B), and Asia Pacific (12B), reflecting broad international exposure within Information Technology Services.
Revenue by Segment
This pie chart illustrates IBM’s revenue distribution by segment for the full fiscal year 2024, highlighting the company’s primary business drivers.
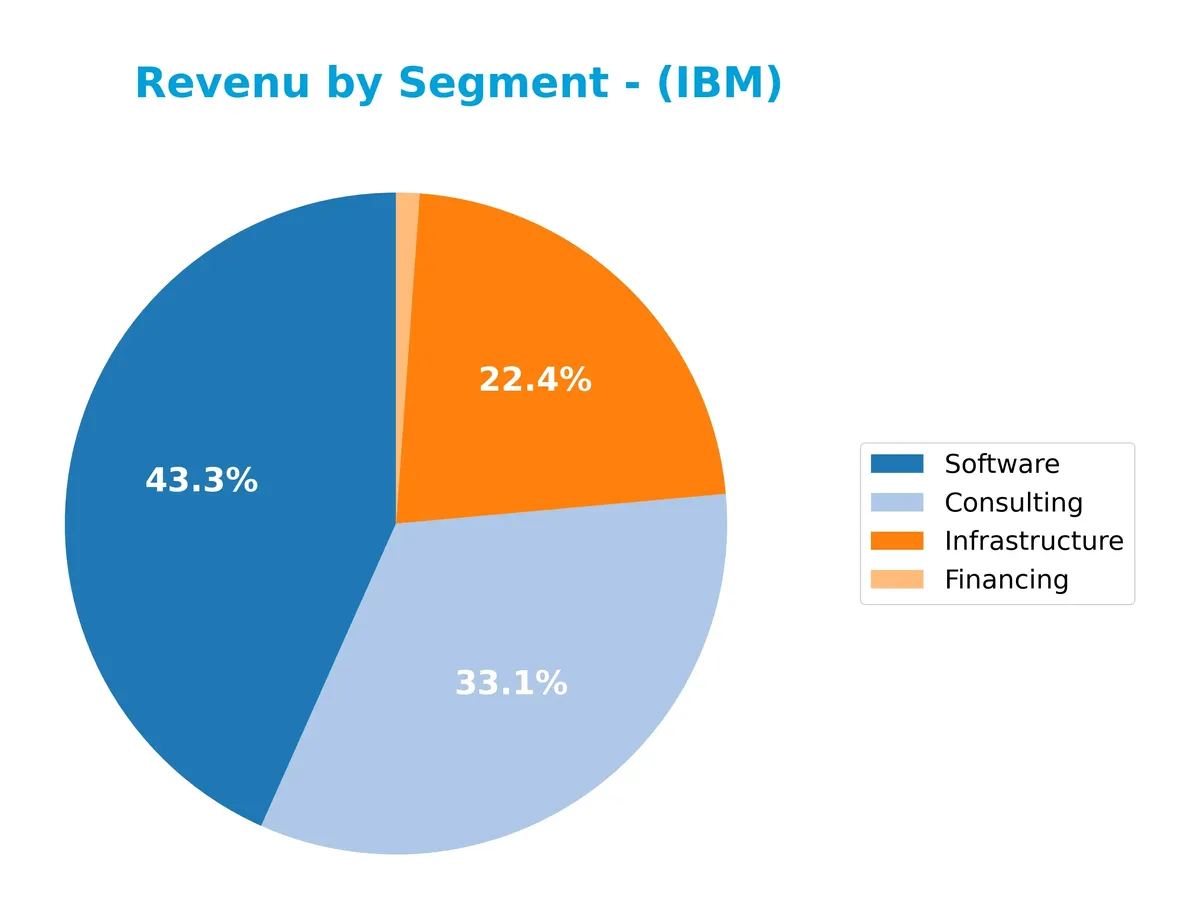
In 2024, Software leads IBM’s revenue at 27.1B, followed by Consulting at 20.7B and Infrastructure at 14.0B. Financing contributes marginally with 713M. Software shows steady growth, signaling IBM’s focus on high-margin, scalable solutions. The slight decline in Infrastructure suggests a shift from traditional hardware services. Consulting remains robust, underscoring IBM’s emphasis on advisory and integration services, balancing the portfolio well.
Key Products & Brands
The table below summarizes IBM’s key products and brands along with brief descriptions:
| Product | Description |
|---|---|
| Software | Hybrid cloud platforms, business automation, AI, security, transaction processing, including Red Hat. |
| Consulting | Business transformation, strategy, data analytics, system integration, technology, and cloud services. |
| Infrastructure | On-premises and cloud servers, storage solutions, hybrid cloud support, and equipment remarketing. |
| Financing | Lease, installment, loan, and short-term working capital financing services. |
IBM’s revenue streams focus on software and consulting, reflecting a shift towards integrated IT services and hybrid cloud solutions. Infrastructure remains vital for mission-critical workloads, while financing supports client operational needs.
Main Competitors
The sector includes 16 competitors, with the table showing the top 10 leaders by market capitalization:
| Competitor | Market Cap. |
|---|---|
| International Business Machines Corporation | 272B |
| Accenture plc | 162B |
| Cognizant Technology Solutions Corporation | 40B |
| Fiserv, Inc. | 36B |
| Fidelity National Information Services, Inc. | 34B |
| Wipro Limited | 30B |
| Leidos Holdings, Inc. | 23B |
| Gartner, Inc. | 18B |
| CDW Corporation | 17B |
| Jack Henry & Associates, Inc. | 13B |
International Business Machines Corporation ranks first among 16 competitors in the Information Technology Services sector. Its market cap is 99.45% of the top player’s scale, effectively making it the leader. The company stands well above both the average market cap of the top 10 (64.6B) and the sector median (17.8B). It enjoys a significant 67.24% gap from its nearest competitor below.
Comparisons with competitors
Check out how we compare the company to its competitors:
Does IBM have a competitive advantage?
IBM presents a sustainable competitive advantage, evidenced by a ROIC exceeding WACC by 2.23% and a 36% growth trend in ROIC from 2021 to 2025. This indicates efficient capital use and value creation.
The company’s diverse segments in software, consulting, infrastructure, and financing provide growth opportunities. Continued expansion in hybrid cloud, AI solutions, and global markets supports a positive future outlook.
SWOT Analysis
This analysis highlights IBM’s core competitive factors and challenges to guide strategic decisions.
Strengths
- strong brand and global presence
- diversified business segments
- favorable ROIC vs. WACC indicating value creation
Weaknesses
- low current ratio signals liquidity risk
- high debt-to-equity ratio increases financial leverage
- valuation metrics (PE, PB) are relatively expensive
Opportunities
- growth in hybrid cloud and AI markets
- expanding consulting services in digital transformation
- leveraging open-source software ecosystem
Threats
- intense competition in IT services
- rapid technology changes require constant innovation
- economic cycles impacting enterprise spending
IBM’s robust competitive moat and growing profitability position it well. However, liquidity and leverage risks require caution. Strategic focus on cloud and AI can drive sustainable growth amid sector challenges.
Stock Price Action Analysis
The weekly stock chart below illustrates International Business Machines Corporation’s price movements and volatility patterns over the past 12 months:
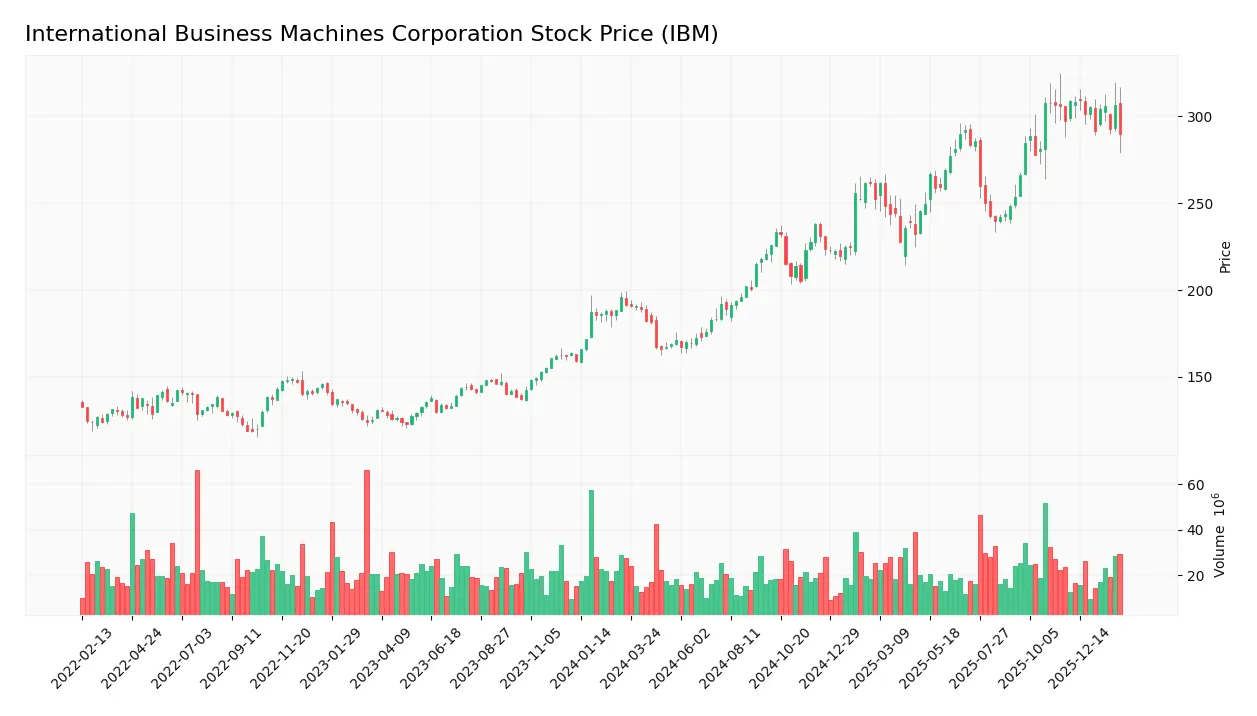
Trend Analysis
Over the past 12 months, IBM’s stock gained 51.76%, indicating a strong bullish trend. The price peaked at 309.24 and bottomed at 165.71, showing high volatility with a 43.47 standard deviation. Recently, from November 2025 to February 2026, the trend reversed slightly, dropping 2.51% with decelerating momentum.
Volume Analysis
Total volume rose steadily to 2.58B shares, with buyers accounting for 57.5%, signaling buyer-driven activity overall. However, in the recent three months, seller volume surpassed buyer volume, with buyer dominance at 45.12%, suggesting a slight seller advantage and cautious investor sentiment.
Target Prices
Analysts set a consensus target price reflecting moderate optimism for IBM’s near-term valuation.
| Target Low | Target High | Consensus |
|---|---|---|
| 304 | 380 | 349.5 |
The target range suggests expectations of upside potential around 10-15% above current levels, signaling confidence in IBM’s strategic execution.
Don’t Let Luck Decide Your Entry Point
Optimize your entry points with our advanced ProRealTime indicators. You’ll get efficient buy signals with precise price targets for maximum performance. Start outperforming now!
Analyst & Consumer Opinions
This section examines International Business Machines Corporation’s grades and consumer feedback to provide a balanced perspective.
Stock Grades
Here are the most recent verified analyst grades for International Business Machines Corporation (IBM) from established firms:
| Grading Company | Action | New Grade | Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| UBS | Maintain | Sell | 2026-01-29 |
| Jefferies | Maintain | Buy | 2026-01-29 |
| JP Morgan | Maintain | Neutral | 2026-01-29 |
| RBC Capital | Maintain | Outperform | 2026-01-29 |
| Wedbush | Maintain | Outperform | 2026-01-29 |
| Stifel | Maintain | Buy | 2026-01-29 |
| Evercore ISI Group | Maintain | Outperform | 2026-01-29 |
| JP Morgan | Maintain | Neutral | 2026-01-21 |
| Evercore ISI Group | Maintain | Outperform | 2026-01-20 |
| B of A Securities | Maintain | Buy | 2026-01-13 |
Overall, the grades show a broad consensus maintaining positive outlooks, with multiple Outperform and Buy ratings. However, a minority of Sell and Neutral ratings reveal some caution among analysts.
Consumer Opinions
Consumer sentiment around IBM reveals a mix of appreciation for its innovation and frustration over service consistency.
| Positive Reviews | Negative Reviews |
|---|---|
| “IBM’s technology solutions boost our efficiency significantly.” | “Customer support response times are often slow.” |
| “Strong commitment to research and development.” | “Pricing can be opaque and sometimes high.” |
| “Reliable cloud services with robust security.” | “Occasional software bugs disrupt workflows.” |
Overall, consumers praise IBM’s innovation and security focus. However, service responsiveness and pricing transparency emerge as notable pain points.
Risk Analysis
Below is a summary table of key risks facing IBM, including probability and impact assessments:
| Category | Description | Probability | Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| Leverage Risk | High debt-to-equity ratio (2.06) raises financial risk | High | High |
| Liquidity Risk | Current ratio below 1 (0.93) signals potential short-term stress | Medium | Medium |
| Valuation Risk | Elevated P/E (26.07) and P/B (8.46) suggest overvaluation | Medium | Medium |
| Operational Risk | Asset turnover low (0.44), indicating possible inefficiencies | Medium | Low |
| Market Risk | Beta below 1 (0.69) limits volatility but reduces upside potential | Low | Medium |
IBM’s most pressing risk lies in its high leverage. Historically in tech services, elevated debt burdens increase vulnerability during market downturns. The current ratio under 1 hints at liquidity constraints, a red flag for short-term obligations. Despite favorable returns on equity and capital, valuation metrics appear stretched compared to the S&P 500 average, raising caution for new investors.
Should You Buy International Business Machines Corporation?
International Business Machines Corporation appears to be improving profitability with a durable competitive moat supported by growing ROIC. Despite a substantial leverage profile signaling financial risk, the overall B rating suggests a moderately favorable investment profile with prudent caution advised.
Strength & Efficiency Pillars
International Business Machines Corporation (IBM) exhibits strong profitability with a net margin of 15.69% and a return on equity of 32.45%. The company’s ROIC stands at 8.57%, surpassing its WACC of 6.34%, marking it as a clear value creator. IBM’s Altman Z-Score of 3.47 places it safely away from bankruptcy risk, while a Piotroski Score of 5 signals moderate financial health. These metrics underscore IBM’s ability to generate returns above capital costs and maintain financial stability amid evolving market conditions.
Weaknesses and Drawbacks
IBM’s valuation appears stretched, with a price-to-earnings ratio of 26.07 and a price-to-book ratio of 8.46, indicating premium pricing that may pressure future returns. The firm’s leverage is concerning; a debt-to-equity ratio of 2.06 and a current ratio below 1 at 0.93 suggest liquidity constraints and elevated financial risk. Additionally, recent market behavior shows a slight seller dominance with buyers representing only 45.12%, hinting at short-term headwinds despite overall bullish momentum.
Our Verdict about International Business Machines Corporation
IBM’s long-term fundamentals are favorable, demonstrating sustainable competitive advantages and solid profitability. However, recent market pressure and stretched valuation metrics suggest caution. Despite its value-creating profile, the company might appear best approached with a wait-and-see stance for a more attractive entry point as short-term selling persists. Investors could consider IBM for long-term exposure once valuation and liquidity concerns ease.
Disclaimer: This content is for informational purposes only and does not constitute financial, investment, or other professional advice. Investing in financial markets involves a significant risk of loss, and past performance is not indicative of future results.
Additional Resources
- Savant Capital LLC Purchases 2,456 Shares of International Business Machines Corporation $IBM – MarketBeat (Feb 05, 2026)
- IBM | Founding, History, & Products | Britannica Money – Britannica (Feb 02, 2026)
- Here’s What Analysts Are Saying About International Business Machines (IBM) – Yahoo Finance (Feb 03, 2026)
- IBM to Support Missile Defense Agency SHIELD Contract – Finviz (Feb 05, 2026)
- International Business Machines Corporation (IBM): A Bull Case Theory – Insider Monkey (Feb 04, 2026)
For more information about International Business Machines Corporation, please visit the official website: ibm.com




